presence of glucose and ketone bodies in urine respectively called Urine analysis: part 27 – urine for ketones, and ketone bodies
Welcome to our post on urine analysis and the Glucose Ketone Index (GKI). In this article, we will explore the significance of urine analysis in determining various chemical components as well as the importance of the Glucose Ketone Index in assessing metabolic health.
Urine Analysis and Chemical Examination
 Urine analysis plays a crucial role in assessing your overall health and diagnosing medical conditions. It provides valuable information about the chemical composition of your urine, which can help identify a range of abnormalities and diseases.
Urine analysis plays a crucial role in assessing your overall health and diagnosing medical conditions. It provides valuable information about the chemical composition of your urine, which can help identify a range of abnormalities and diseases.
The chemical examination of urine involves analyzing various substances present in urine, such as glucose, ketones, proteins, blood cells, and pH levels. By evaluating these components, healthcare professionals can gain insights into kidney function, hydration status, and potential underlying medical conditions.
Interpreting the results of a urine analysis requires expertise, as it involves understanding the normal reference ranges and identifying any deviations. Abnormal findings in urine analysis might indicate urinary tract infections, kidney diseases, liver disorders, or metabolic abnormalities.
The Glucose Ketone Index (GKI)
 The Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) is a metric used to assess metabolic health and evaluate the body’s utilization of glucose and ketones as fuel sources. It is particularly relevant in the context of ketogenic diets and therapeutic fasting.
The Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) is a metric used to assess metabolic health and evaluate the body’s utilization of glucose and ketones as fuel sources. It is particularly relevant in the context of ketogenic diets and therapeutic fasting.
The GKI is calculated by dividing the blood glucose level (measured in milligrams per deciliter, mg/dL) by the blood ketone level (measured in millimoles per liter, mmol/L). The resulting ratio provides valuable information about the body’s state of ketosis, with lower GKI values indicating deeper ketosis.
Monitoring the GKI can help individuals following a ketogenic diet or practicing intermittent fasting to optimize their metabolic state and achieve specific health goals. For example, a lower GKI may be associated with increased fat burning, improved cognitive function, and better weight management.
Although the interpretation of GKI values may vary depending on individual circumstances, consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian experienced in ketogenic diets can provide personalized guidance and recommendations.
In conclusion, urine analysis and the Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) are valuable tools in assessing metabolic health and identifying potential abnormalities. Regular monitoring and interpretation of urine analysis results, along with tracking GKI values, can provide insight into overall well-being and help individuals make informed decisions about their health and nutrition.
If you are looking for The Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) Explained - Heather Cooan you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Images about The Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) Explained - Heather Cooan like Urine Analysis: Part 27 – Urine for ketones, and Ketone Bodies, The Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) Explained - Heather Cooan and also Urine Analysis: Part 27 – Urine for ketones, and Ketone Bodies. Here it is:
The Glucose Ketone Index (GKI) Explained - Heather Cooan
 heathercooan.comketone glucose ketones heathercooan
heathercooan.comketone glucose ketones heathercooan
Urine Analysis: Part 27 – Urine For Ketones, And Ketone Bodies
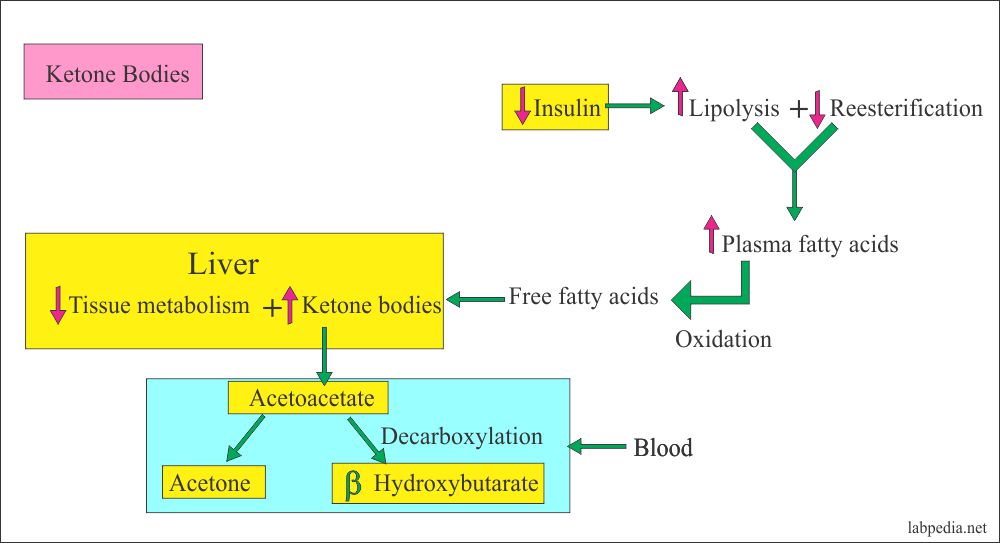
 www.labpedia.netketone bodies ketones formation urine analysis part labpedia metabolism
www.labpedia.netketone bodies ketones formation urine analysis part labpedia metabolism
Urine Analysis: Part 27 – Urine For Ketones, And Ketone Bodies
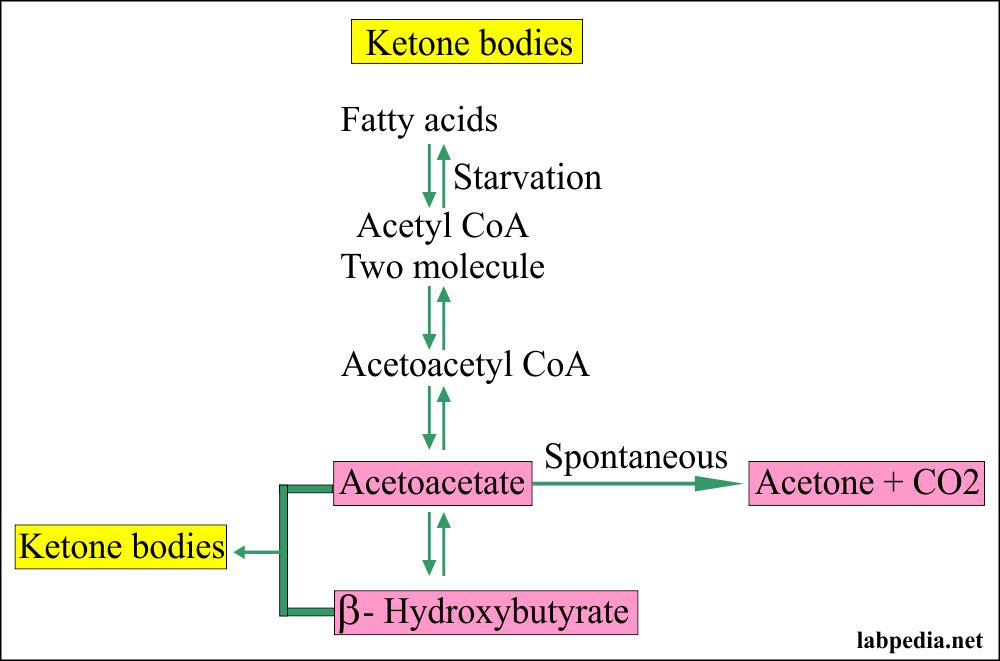
 www.labpedia.neturine ketone ketones ketonuria labpedia
www.labpedia.neturine ketone ketones ketonuria labpedia
Urine Analysis – Part 5 – Urine Analysis, Chemical Examination And
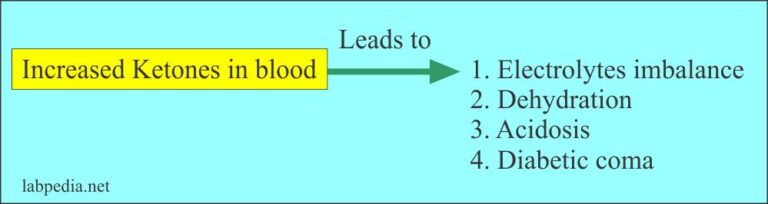
 www.labpedia.netketone ketoacidosis diabetic urine diagnosis labpedia examination interpretations
www.labpedia.netketone ketoacidosis diabetic urine diagnosis labpedia examination interpretations
Ketones In Urine Causes, Normal Values, Test Procedure
 healthsaline.comurine ketones ketone causes body normal
healthsaline.comurine ketones ketone causes body normal
Ketones in urine causes, normal values, test procedure. Ketone ketoacidosis diabetic urine diagnosis labpedia examination interpretations. Urine analysis: part 27 – urine for ketones, and ketone bodies